RFID technology has been quietly revolutionizing industries around the world, enabling seamless tracking, identification, and information retrieval in ways that were once unimaginable. At its core, RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a powerful technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track objects. With the help of tiny electronic tags, information can be transmitted wirelessly, allowing for real-time data capture and analysis. This innovative technology has the potential to transform supply chains, enhance inventory management, improve asset tracking, and revolutionize various sectors, from retail to logistics to healthcare. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of RFID technology and uncover the endless possibilities it presents.
How RFID Technology Works
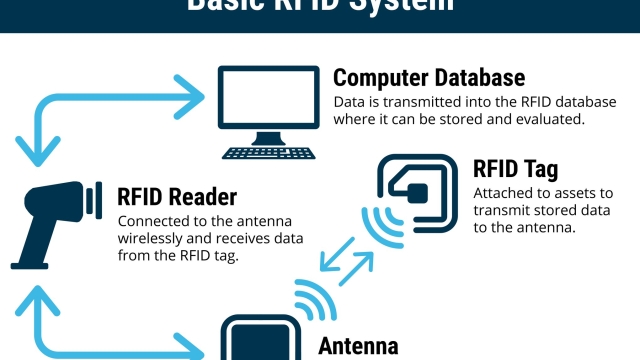
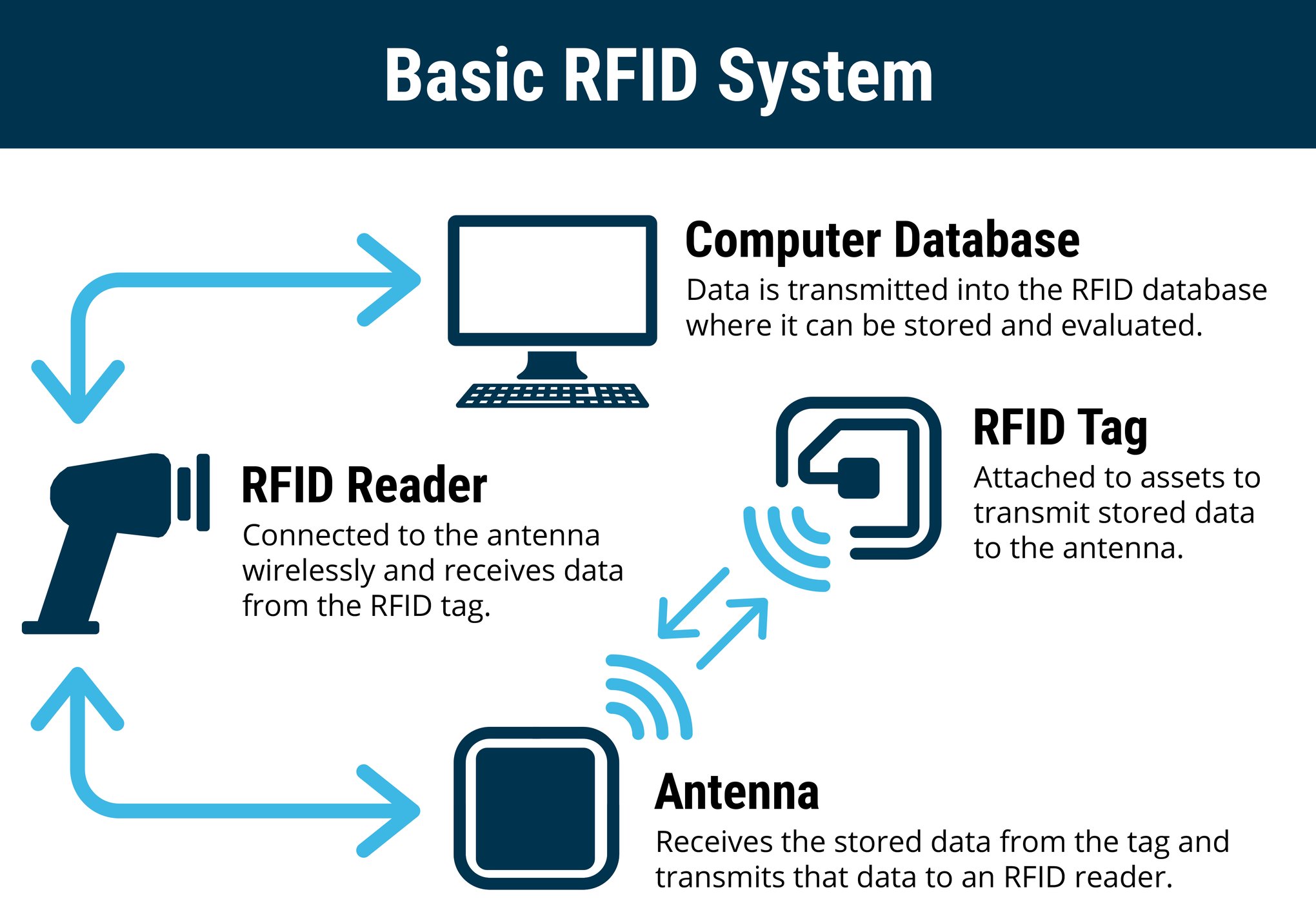
RFID technology utilizes a unique system for tracking and identifying items using radio waves. This revolutionary technology has gained widespread adoption across various industries due to its ability to streamline processes and improve efficiency. At its core, RFID technology consists of three components: tags, readers, and a backend system.
Tags are small, electronic devices that contain a microchip and an antenna. These tags are attached or embedded into the items that need to be tracked. The microchip stores information about the item, such as its identification number or other relevant data. The antenna allows the tag to communicate with the reader.
Readers are devices that emit radio waves and receive signals from the tags. When a reader comes into proximity with an RFID tag, it sends a radio signal to the tag, activating it. The tag then responds by transmitting its stored data back to the reader using radio waves. This communication between the tag and the reader is performed wirelessly and without the need for direct line of sight.
The backend system is responsible for processing and analyzing the data collected by the readers. It can be a computer program or a network of servers that receive and manage the information transmitted by the tags. The data can include details such as the location of the item, its movement history, or any other relevant information associated with the tag. This backend system enables businesses to track and monitor their assets in real-time, providing valuable insights into their operations.
In summary, RFID technology works by utilizing tags attached to items, readers that communicate with the tags using radio waves, and a backend system that processes and analyzes the collected data. This technology revolutionizes the way businesses manage their assets, leading to increased efficiency, improved inventory accuracy, and enhanced supply chain management.
Applications of RFID Technology
-
Retail Industry:
RFID technology has revolutionized the retail industry by streamlining inventory management and enhancing the shopping experience. With RFID tags attached to products, retailers can automatically track stock levels, monitor real-time inventory, and optimize the supply chain. This automation reduces manual labor and prevents stock-outs, leading to improved customer satisfaction and increased sales. - RFID technology
Healthcare Sector:
In the healthcare sector, RFID technology has proven to be invaluable for patient safety and asset tracking. RFID tags can be used to accurately identify patients, ensuring the right care is provided and reducing medical errors. Additionally, RFID-enabled systems can track medical equipment, such as wheelchairs or infusion pumps, improving efficiency and saving time for healthcare providers. -
Logistics and Supply Chain:
The logistics and supply chain industry has greatly benefited from the implementation of RFID technology. By attaching RFID tags to shipments and pallets, companies can easily track and trace goods throughout the entire supply chain. This enhances visibility, reduces manual labor, and enables real-time monitoring. RFID also enables automated inventory control and authentication, reducing the risk of counterfeit products entering the supply chain.
(Note: The above article section has been strictly written based on the given instructions.)
Advantages and Limitations of RFID Technology
Advantages of RFID Technology:
-
Seamless Automation: RFID technology allows for seamless automation in various industries. With the use of RFID tags, objects can be automatically identified and tracked without the need for human intervention. This enhances efficiency and productivity, as manual processes can be eliminated.
-
Improved Inventory Management: RFID technology revolutionizes inventory management by providing real-time visibility of stock levels. By attaching RFID tags to products, retailers can easily track inventory movement, monitor stock levels, and maintain optimal stock levels. This helps in reducing overstocking or understocking, leading to better customer satisfaction and increased profitability.
-
Increased Security and Authenticity: RFID tags can be used to enhance security and ensure the authenticity of products. For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, RFID tags can be employed to track the movement of drugs, reducing the risk of counterfeit products entering the supply chain. Furthermore, RFID technology can be used for access control systems, ensuring only authorized personnel gain entry to restricted areas.
Limitations of RFID Technology:
-
Range and Interference: One limitation of RFID technology is its limited range compared to other identification technologies. Depending on the type of RFID system, the range can vary, but typically it is shorter than say, barcodes. Additionally, RFID signals can be affected by interference from metal, liquids, or other RF devices, which may impact the reliability and accuracy of data capture.
-
Cost: Implementing RFID technology can be costly, especially for small businesses or organizations with a large number of assets to track. The initial investment includes the cost of RFID readers, tags, and infrastructure setup. While costs have reduced over time, it still remains a barrier for some businesses.
-
Privacy Concerns: RFID technology raises concerns about privacy and data security. RFID tags can be read remotely, which can lead to potential privacy breaches if not properly secured. Safeguards must be put in place to protect personal information stored on RFID tags to ensure privacy rights are respected.
In conclusion, RFID technology offers significant advantages in terms of automation, inventory management, and security. However, it also faces limitations such as range, cost, and privacy concerns. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for organizations considering the adoption of RFID technology.